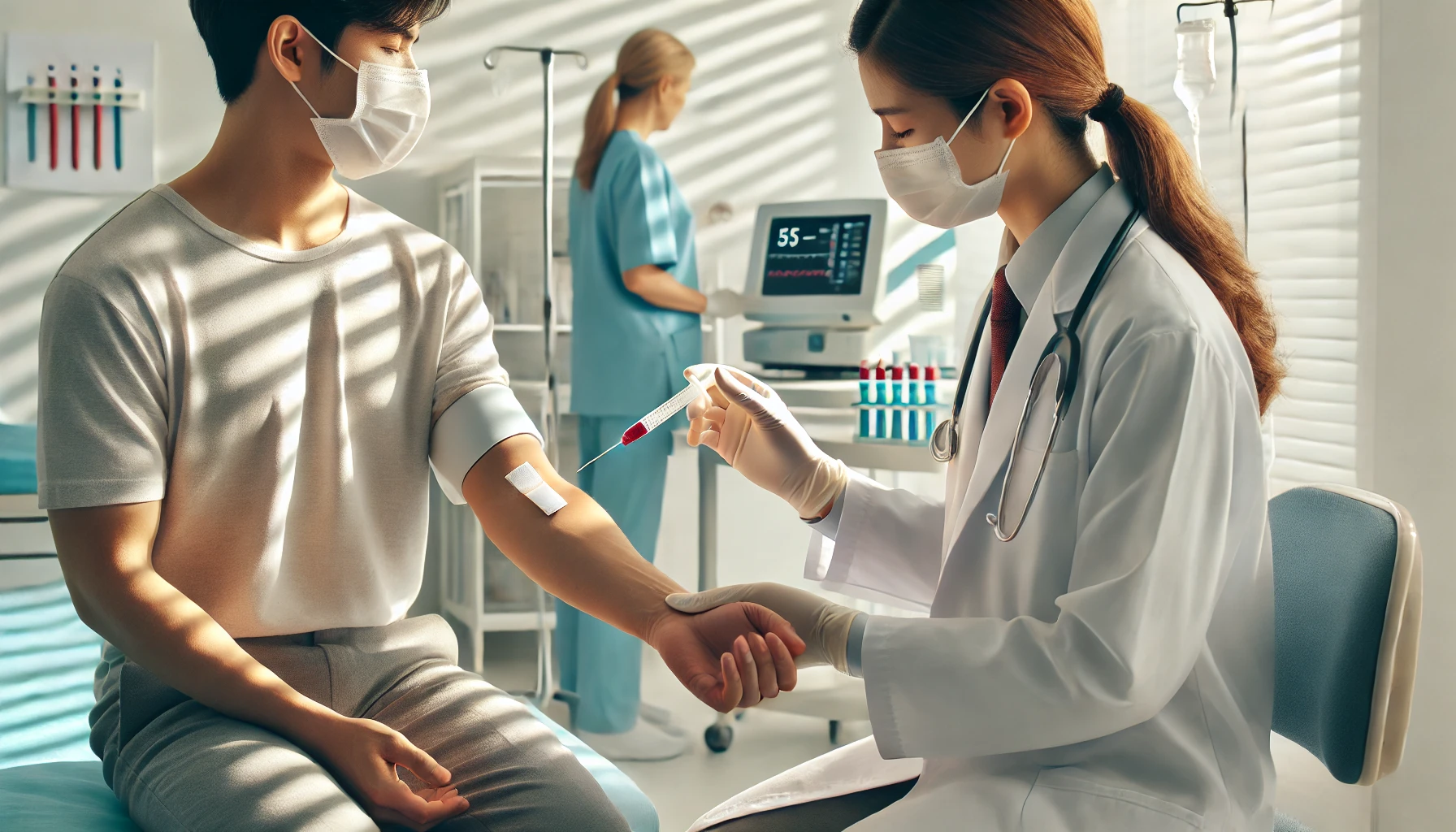
The FNAC test, or Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology, is a widely used diagnostic procedure that helps identify various medical conditions. This minimally invasive technique involves using a thin needle to extract a small sample of tissue or fluid from a lump or swelling. By examining the sample under a microscope, healthcare professionals can determine the nature of the abnormality, whether benign or malignant.
This procedure is crucial in diagnosing and managing conditions such as tumors, cysts, and infections. Let’s delve deeper into the details of the FNAC test, its procedure, benefits, and more.
What Is an FNAC Test?
An FNAC test is a diagnostic procedure that uses a fine needle to collect cells from a suspicious area in the body. It is often recommended when a lump, swelling, or mass is detected, and further investigation is required to determine its nature. This test provides valuable information quickly and with minimal discomfort, making it a preferred choice for both doctors and patients.
Why Is an FNAC Test Performed?
The FNAC test serves several purposes, including:
- Diagnosing Tumors: Differentiates between benign and malignant growths.
- Investigating Swellings: Helps identify the cause of unexplained swellings, particularly in areas like the neck, breast, or thyroid.
- Detecting Infections: Identifies bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
- Monitoring Chronic Conditions: Assists in tracking the progress of certain diseases, such as lymphomas or tuberculosis.
By providing a quick and accurate diagnosis, the FNAC test plays a vital role in formulating an effective treatment plan.
How Is the FNAC Test Performed?
Pre-Test Preparation
Before undergoing an FNAC test, patients are typically advised to follow basic instructions. These may include:
- Informing the Doctor: Share any ongoing medications or allergies.
- Avoiding Blood Thinners: If prescribed, these medications might need to be paused temporarily.
- Wearing Comfortable Clothing: Ensures ease during the procedure.
No significant preparation is usually required, making the FNAC test convenient for patients.
The Procedure
The FNAC test is performed in a clinical setting and usually takes less than 30 minutes. Here’s what to expect:
- Positioning the Patient: The patient is positioned comfortably, depending on the area being examined.
- Cleaning the Site: The skin over the lump or swelling is cleaned with an antiseptic.
- Insertion of the Needle: A fine, hollow needle is gently inserted into the lump or swelling.
- Sample Collection: The doctor uses a syringe to extract a small sample of cells or fluid.
- Bandaging: After the needle is removed, a small bandage is applied to the site.
Post-Procedure Care
After the FNAC test, patients can usually resume normal activities immediately. Some mild soreness or bruising may occur at the site, but this typically resolves within a few days.
Benefits of the FNAC Test
Minimally Invasive
The FNAC test is less invasive than traditional biopsy methods, requiring only a thin needle. This reduces the risk of complications and speeds up recovery time.
Quick Results
In most cases, results from an FNAC test are available within a few days. This allows for faster diagnosis and timely initiation of treatment.
Cost-Effective
Compared to other diagnostic procedures, the FNAC test is relatively affordable, making it accessible to a wide range of patients.
High Accuracy
When performed correctly, the FNAC test offers a high degree of accuracy in diagnosing various conditions, including cancers and infections.
Conditions Diagnosed by FNAC Test
The FNAC test is instrumental in diagnosing a wide range of conditions, including:
- Thyroid Disorders: Helps detect goiters, nodules, and thyroid cancers.
- Breast Lumps: Differentiates between benign cysts and malignant tumors.
- Lymph Node Swellings: Identifies causes such as infections, lymphomas, or metastases.
- Salivary Gland Issues: Detects tumors or infections in salivary glands.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Lesions: Evaluates unexplained lumps or growths in soft tissues.
Limitations of the FNAC Test
Despite its many advantages, the FNAC test does have some limitations:
- Sample Size: The small sample size may not always provide a comprehensive view of the abnormality.
- Need for Additional Tests: In some cases, further diagnostic procedures like core biopsy or imaging studies may be required.
- False-Negative Results: Although rare, there is a small risk of obtaining false-negative results, especially if the sample is inadequate.
Comparing FNAC Test with Other Diagnostic Procedures
FNAC vs. Biopsy
While both FNAC and biopsy involve collecting tissue samples, the methods and purposes differ:
- FNAC: Uses a fine needle, less invasive, quicker results.
- Biopsy: Involves a larger tissue sample, more invasive, provides detailed analysis.
FNAC vs. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans provide visual information about abnormalities. However, FNAC offers cellular-level insights, helping to confirm or refine a diagnosis.
How to Interpret FNAC Test Results
The results of an FNAC test are typically categorized as follows:
- Non-Diagnostic: Insufficient sample, requiring a repeat test.
- Benign: Non-cancerous growths or infections.
- Suspicious: Further investigation needed to confirm malignancy.
- Malignant: Indicates cancerous cells, requiring immediate attention.
Your healthcare provider will discuss the results and suggest appropriate next steps.
FAQs
What is an FNAC test used for?
An FNAC test helps diagnose lumps, swellings, and tumors by collecting and examining cells from the affected area.
Is the FNAC test painful?
The procedure involves minimal discomfort, similar to a regular injection. Any soreness usually subsides quickly.
How long do FNAC test results take?
Results are generally available within 1-3 days, depending on the complexity of the analysis.
Can FNAC detect cancer?
Yes, FNAC is effective in detecting cancer cells, though further tests may be required for a detailed diagnosis.
Is FNAC safe for all patients?
FNAC is safe for most individuals, including those with chronic conditions, as it is minimally invasive.
What should I avoid before an FNAC test?
Inform your doctor about any medications, especially blood thinners, and follow their specific instructions.
Can FNAC results be inconclusive?
In some cases, the sample may be inadequate, leading to inconclusive results. A repeat test or additional procedures may be needed.
Conclusion
The FNAC test is an essential tool in modern medicine, offering a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and accurate method for diagnosing various conditions. Whether it’s investigating a suspicious lump or monitoring a chronic disease, this procedure provides valuable insights that guide effective treatment. By understanding the FNAC test and its benefits, patients can approach their healthcare journey with confidence.